- Etiology: mesothelial-lined peritoneal surfaces failing to coalesce, arises from root of mesentery
- US: thin walled simple cyst with posterior acoustic enhancement
Radiology Cases of Mesenteric Cyst

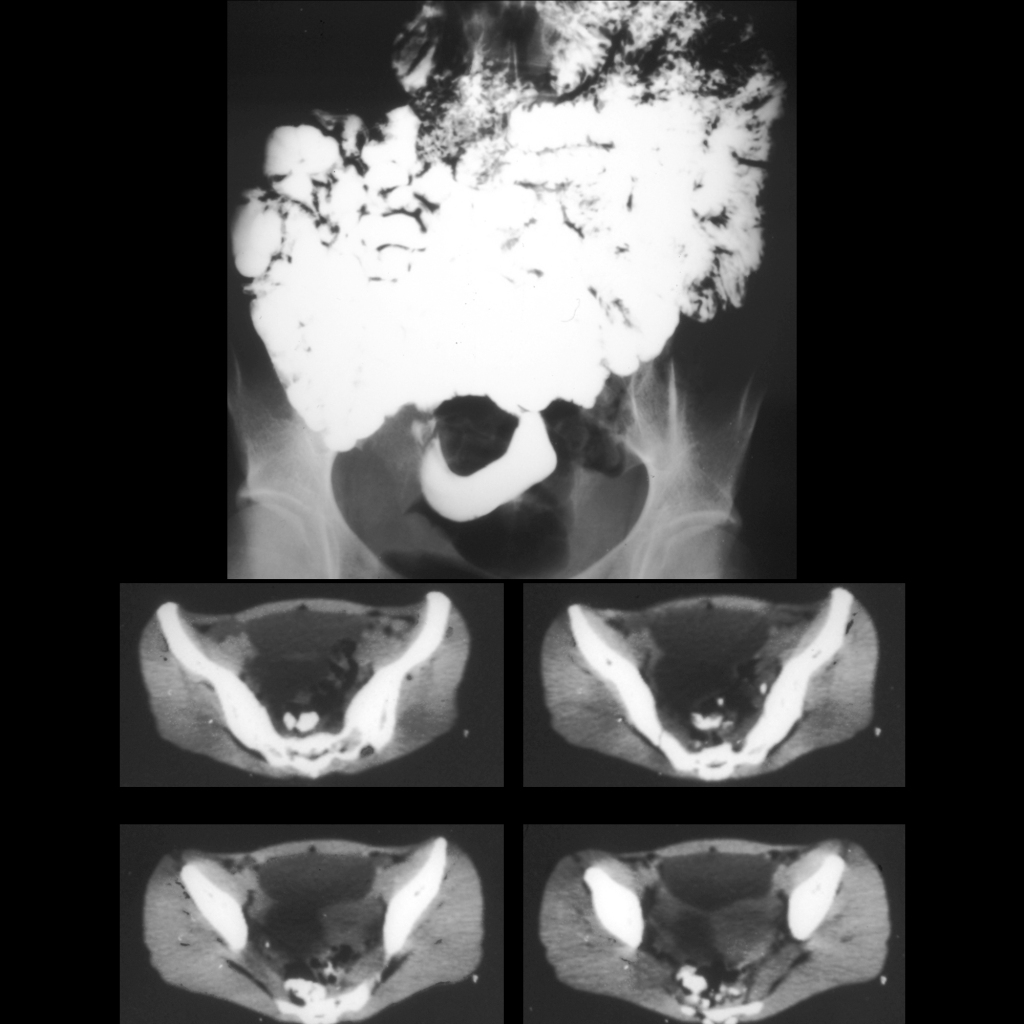
Radiology Case of Mesenteric Cyst Causing Small Bowel Volvulus
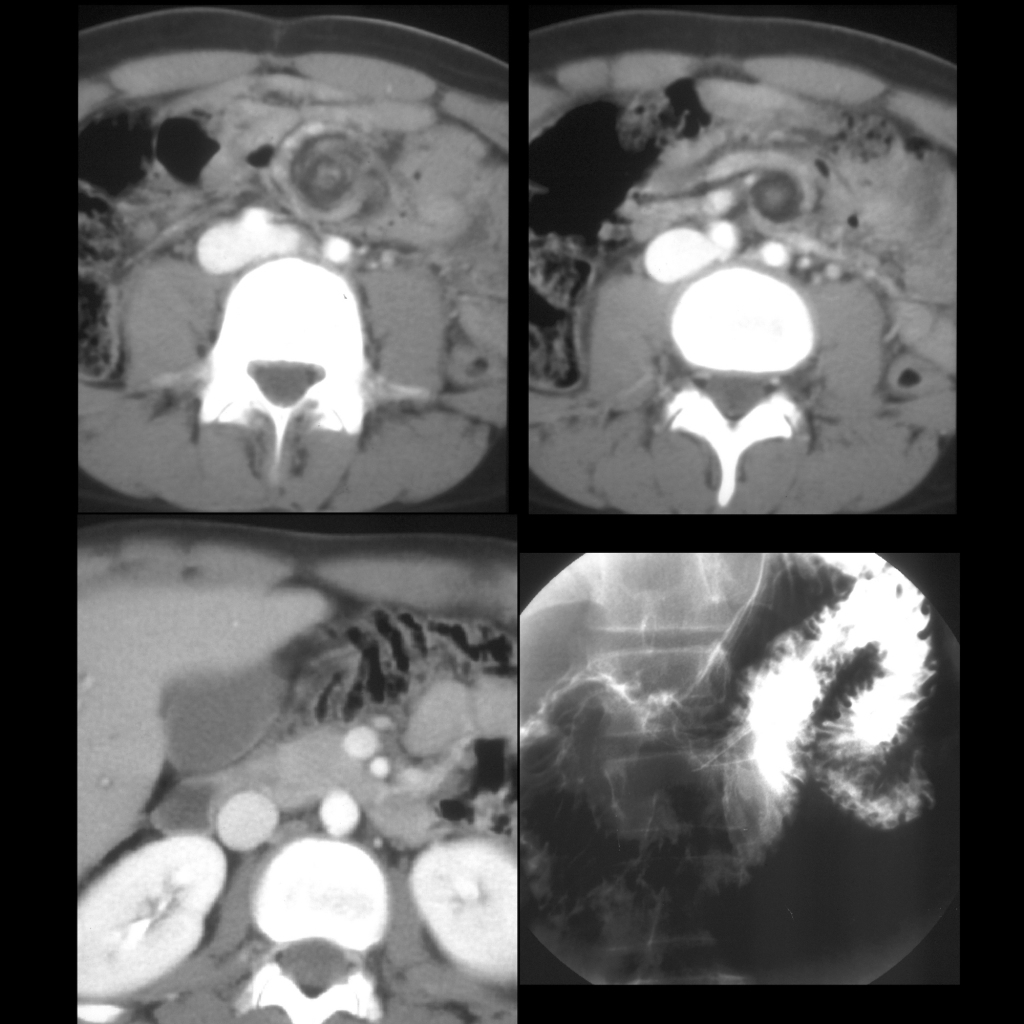
Surgery Cases of Mesenteric Cyst

