Indonesian zoo breeds dozens of endangered baby Komodo dragons
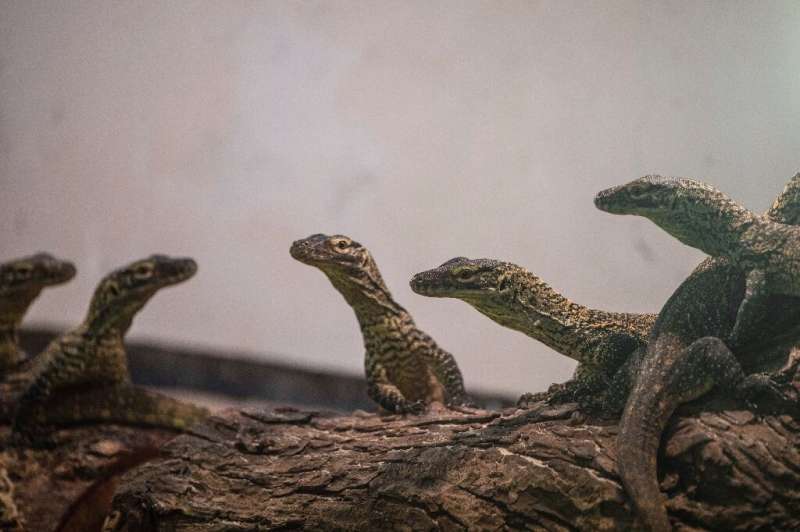

An Indonesian zoo has welcomed dozens of new baby Komodo dragons hatched in captivity in recent months as part of a breeding programme, its director said Tuesday, offering hope for efforts to conserve the endangered species.
The world's largest living lizards are found only in Indonesia's World Heritage-listed Komodo National Park and neighbouring Flores, and just 3,458 adult and baby species are left in the wild according to estimates.
The fearsome reptiles, which can grow to three metres (10 feet) in length and weigh up to 90 kilograms (200 pounds), are threatened by human activity and climate change destroying their habitat.
But a breeding programme in Indonesia's second-largest city of Surabaya is trying to change that, successfully breeding 29 dragons in incubators between February and March.
"We have habitats that mirror the Komodo's natural habitat, including its humidity and temperature," zoo director Chairul Anwar told AFP.
The newborns were hatched from two female Komodo dragons after their eggs were placed in incubators to prevent them from being eaten by their mothers or other Komodo dragons.
Female Komodos can fertilise an egg without the need for a male dragon.
The zoo started the programme in the 1990s as part of the effort to conserve the species in a city located more than 700 kilometres (434 miles) away from the dragon's natural habitat.
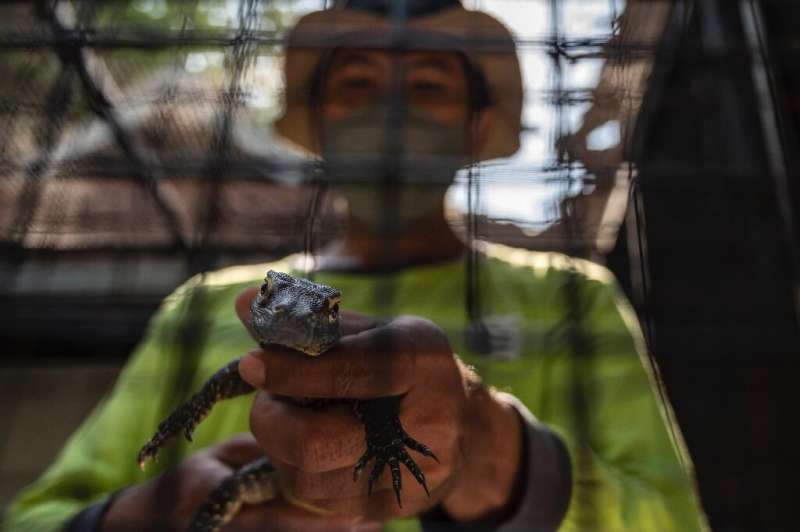

After the spate of births this year, Surabaya Zoo now houses 134 Komodo dragons, the largest population group outside of its habitat in the cluster of islands east of Bali, Anwar said.
In a report last year, the International Union for the Conservation of Nature warned the endangered species' habitat was expected to shrink by 30 percent in the next 45 years due to rising sea levels.
Anwar said the dragons will not be released back into the wild on Komodo or Flores until conditions improve.
"Komodo Island is still working to rejuvenate the forests," which feed the dragon's declining natural prey such as deer, he said.
© 2022 AFP