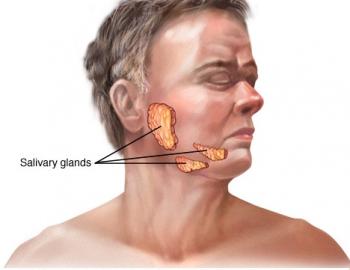
Mumps is a viral infection that primarily affects saliva-producing (salivary) glands that are located near your ears. Mumps can cause swelling in one or both of these glands.
Mumps was common in the United States until mumps vaccination became routine. Since then, the number of cases has dropped dramatically.
However, mumps outbreaks still occur in the United States, and the number of cases has crept up in recent years. These outbreaks generally affect people who aren't vaccinated, and occur in close-contact settings such as schools or college campuses.
Complications of mumps, such as hearing loss, are potentially serious but rare. There's no specific treatment for mumps.
Symptoms
Some people infected with the mumps virus have either no signs or symptoms or very mild ones. When signs and symptoms do develop, they usually appear about two to three weeks after exposure to the virus.
The primary sign of mumps is swollen salivary glands that cause the cheeks to puff out. Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Pain in the swollen salivary glands on one or both sides of your face
- Pain while chewing or swallowing
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Weakness and fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Causes
Mumps is caused by a virus that spreads easily from person to person through infected saliva. If you're not immune, you can contract mumps by breathing in saliva droplets from an infected person who has just sneezed or coughed. You can also contract mumps from sharing utensils or cups with someone who has mumps.
Diagnosis
If you or your child has signs or symptoms of mumps, the doctor is likely to:
- Ask whether you or your child has been vaccinated against mumps and whether you might have been exposed to the virus
- Recommend a blood test to check for evidence of the mumps virus
Treatment
Mumps is caused by a virus, so antibiotics aren't effective. But most children and adults recover from an uncomplicated case of mumps within a few weeks.
People with mumps are generally no longer contagious and can safely return to work or school about five days after the appearance of signs and symptoms.