
Posted on by Miss Jane Olver
The Eye of Horus is an ancient Egyptian symbol known all around the world. It is often worn as a piece of delicate jewellery to protect its wearer and has an exquisitely beautiful shape, often containing colour. It has long been associated with the power of healing, protection, rebirth, wholeness and even resurrection.
The Eye of Horus symbol combines sciences and mythology with art and anatomy. It is sometimes called the all-seeing eye as a reference to the third eye. The third eye is a mystical invisible eye, usually depicted as located on the forehead. In Indian tradition, it is where the Bindi mark is located. The third eye represents the enlightenment which provides perception beyond ordinary sight that is said to be achieved through meditation.
In many homes in the Middle East, you will find the eye of Horus as a decorative item to offer protection from the “evil eye”. It is believed that the eyes are very powerful and can be used for good or bad, and by keeping the Eye of Horus around as the “good eye”, it can counter any evil eye that enters the house. The definition of the evil eye is almost always one of jealously. It is, therefore, a regular gift to someone who has purchased a new home or car or even got married. Women in the Middle East are frequently gifted the Eye of Horus as a piece of jewellery.
Another name for the Eye of Horus is the “Eye of the Mind”. When the Eye of Horus is superimposed over a cross-section of the human brain, each of the six sections of the eye corresponds to one of the major sensory centres.
Ancient Egyptians were known to be leaders in medicine and anatomy. However, what is fascinating is their understanding of the intricate functions of the central nervous system without the presence of modern technology.
The following is a list of each part of the Eye of Horus to sections of the brain:
Smell: The triangular-shaped section on the right side of the eye is located in the olfactory trigone. On closer examination, it may seem to be shaped like a human nose.
Vision: The pupil of the eye corresponds to the interthalamic adhesion.
Humans “see” colours and shapes as vision when the light hits the retina inside the globe. This, in turn, sends neuronal electrical impulses through the optic pathways to the interthalamic adhesion.
Wisdom: The eyebrow corresponds to the shape and location of the corpus callosum.
The eyebrow is indictive of thinking. People tend to move their eyebrows to express various emotions.
Hearing: The triangular left side of the eye corresponds to the location of the Brodman areas 41 and 42, which are the centre of hearing in humans.
Taste: The coil represents the taste pathway in the human brain.
Touch: The teardrop represents the shape and location of the somatosensory pathway; this carries many sensations from the body.
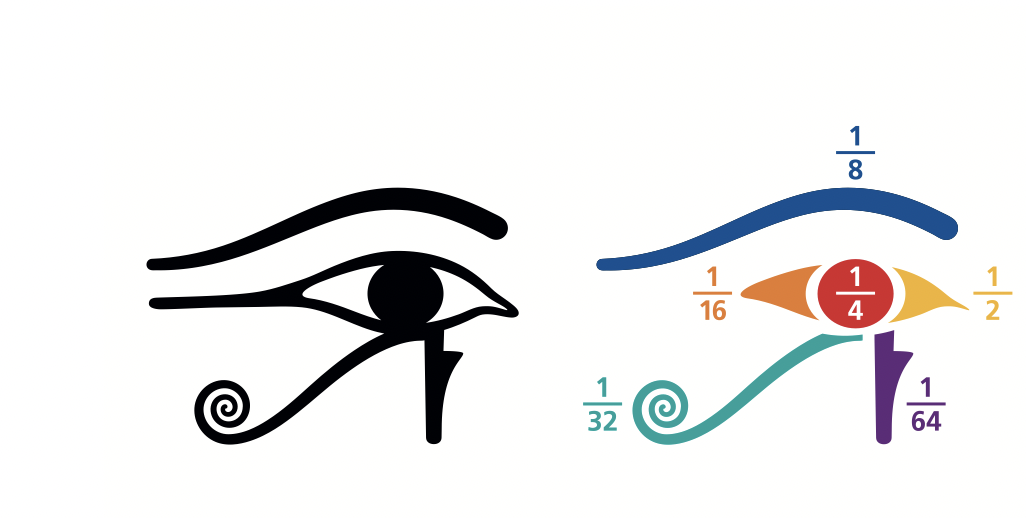
Ancient Egyptians developed complex systems of fractions that are still used today.
Their use of maths was mainly in the arithmetic sense to solve problems. There is evidence to show their outstanding advancement in understanding triangles which makes sense given their ability to build the Pyramids.
The six mathematical parts in the Eye of Horus are 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, and 1/64. The fractions were used to represent the measuring unit that was utilized by the ancient Egyptians for grains and flour.
The Eye of Horus gives a deep understanding of Egyptian medicine and maths capabilities that are truly valuable still today. This ancient civilization still bewilders the modern world as to how it managed to build the Pyramids without modern machinery. It seems there is still much more to learn from ancient Egypt.
As an Ophthalmology and Dermatology Clinic we are all fascinated by the Eye of Horus, its history, symbolism and beauty.
Telephone: 020 7935 7990
International Callers : +44 20 7935 7990