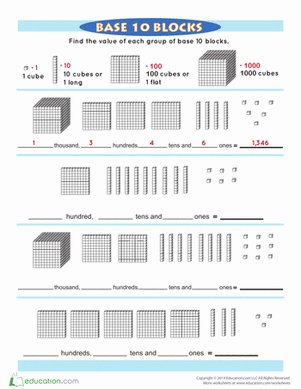
Science project
Acid-Base Catalysis
Your body relies on enzymes. You might be familiar with the enzymes that digest your food, like the salivary amylase in your saliva, but enzymes do all kinds of jobs everywhere in your body. Enzymes are special types of catalysts made of protein. Catalysts help speed up chemical reactions without being used up themselves.
Enzymes are not just found in the human body, they are found in all living things, including yeast. Yeast contains the enzyme catalase (note how the name of many enzymes ends in “–ase”). Catalase breaks down the chemical hydrogen peroxide (H202) into oxygen gas and water. It is easy to see if catalase is working because as it creates oxygen gas, causing bubbles to form.
Now, remember that we said that enzymes are made of proteins? Proteins are important biological compounds. You probably know some foods that are high in protein, like meat and eggs. Have you ever fried an egg? The protein in the liquid egg white changes to a solid white mass when heated, because the heat changes how the protein is put together. This change is permanent. Since enzymes are proteins, they too can be changed by heating. The addition of acids and bases can also affect how a protein is put together. In this investigation, you will treat the catalase enzyme in yeast with acids and bases and then see how well the enzyme is able to break down hydrogen peroxide afterwards.
Problem: How do acids and bases affect enzymes?
Materials
5 Clear glass containers of equal size (beakers or test tubes are ideal)
Permanent marker
Tape
5 Clean spoons
Distilled water
Small cup
Baking soda
Set of measuring teaspoons
Measuring cup
Hydrogen peroxide
Dry yeast
Ruler
Lemon juice
Procedure
Label the containers: 1- Control, 2- Low Acid, 3- High Acid, 4- Low Base, and 5-High Base.
Put a spoon in each of the containers, and make sure to never move a spoon from one container to the other.
Pour a ½ cup of distilled water in the cup.
Add one teaspoons of baking soda, and stir it to dissolve.
Add two teaspoons of distilled water to container 1- Control.
Stir in ¼ cup of hydrogen peroxide to container 1- Control.
Stir in 1/8 teaspoon of yeast.
Place the ruler alongside the container, and record the highest height the bubbles reach
Now that you have an idea of what happens when catalase is added to hydrogen peroxide, predict the height of the bubbles for the other containers which you will treat with acids and bases. Record your predictions.
|
Container |
Predicted bubble height |
Actual Bubble height |
|
1-Control |
|
|
|
2- Low Acid |
|
|
|
3- High Acid |
|
|
|
4-Low Base |
|
|
|
5-High Base |
|
|
Create the acid-treated containers. Add one teaspoon of lemon juice to container 2- Low Acid and two teaspoons of lemon juice to container 3-vHigh Acid.
Add one teaspoon of distilled water to container 2- Low Acid so it is the same volume as container 3.
Stir in ¼ cup of hydrogen peroxide to containers 2 and 3.
Add 1/8 teaspoon yeast to both container 2 and 3. Stir and observe.
Record the maximum height of the yeast bubbles.
Create the base-treated containers. Add one teaspoon of the baking soda solution to container 4- Low Base and two teaspoons of the baking soda solution to container 5- High Base.
Add one teaspoon of distilled water to container 4- Low Base so it has the same volume as container 5.
Stir in ¼ cup of hydrogen peroxide to containers 4 and 5.
Add 1/8 teaspoon yeast to both container 4 and 5. Stir and observe.
Record the maximum height of the yeast bubbles.
Compare your predictions with your actual observations.
Results
The bubble height is likely to be highest is the 1- Control. The bubble height is likely to be higher in both the Low Acid and Low Base than in the High Acid and High Base.
Why?
The catalase enzyme works best around pH 7, which is pH neutral. This indicates that it works best when there is neither excess acid nor base. The addition of a little acid (lemon juice) changes the catalase protein a little, causing it not to work quite as well, whereas the addition of more acid changes the catalase protein more, further reducing its ability to create oxygen bubbles. The addition of a little base (baking soda) changes the catalase protein a bit, causing it not to work quite as well, whereas the addition of double the amount of baking soda further damages the catalase protein.
Going Further
If you want a more accurate picture of what the acid and base are doing in the reaction, use some pH paper to see how the pH is changed. Also, not all enzymes work best at neutral pH. The enzyme lactase evolved to work in the digestive system, where pH’s are not neutral. Do an experiment to determine at what pH level lactase works best.
Education.com provides the Science Fair Project Ideas for informational purposes only. Education.com does not make any guarantee or representation regarding the Science Fair Project Ideas and is not responsible or liable for any loss or damage, directly or indirectly, caused by your use of such information. By accessing the Science Fair Project Ideas, you waive and renounce any claims against Education.com that arise thereof. In addition, your access to Education.com's website and Science Fair Project Ideas is covered by Education.com's Privacy Policy and site Terms of Use, which include limitations on Education.com's liability.
Warning is hereby given that not all Project Ideas are appropriate for all individuals or in all circumstances. Implementation of any Science Project Idea should be undertaken only in appropriate settings and with appropriate parental or other supervision. Reading and following the safety precautions of all materials used in a project is the sole responsibility of each individual. For further information, consult your state's handbook of Science Safety.