What is protein purification?
Protein purification is the process of isolating a specific protein from a complex mixture of proteins, such as a cell lysate. The goal of protein purification is to obtain a highly pure sample of the protein of interest that is free from contaminants, such as other proteins, toxins, lipids, and nucleic acids. This process is essential for many downstream applications, such as structural and functional studies, as well as for the production of purified proteins for therapeutic or industrial use.
Generally, the first step in protein purification is to break the cells open or lyse them, in order to release the proteins into a solution. This is typically done by mechanical methods, such as grinding or sonication, or by chemical methods, such as the use of detergents or enzymes.
Once the proteins are released, the next step is to remove any remaining cellular debris and non-specific proteins. This can be done through centrifugation or filtration.
The next step is to perform a series of purification steps using specific techniques that allow the target protein to be selectively separated from the other proteins in the mixture. These techniques include:
- Precipitation: proteins can be separated based on their solubility properties, such as by adding a precipitant such as ammonium sulfate, or by adjusting the pH or salt concentration.
- Chromatography: proteins can be separated based on their physical and chemical properties, such as their size, charge, or hydrophobicity. Chromatography techniques include ion-exchange, size-exclusion, affinity, and hydrophobic interaction chromatography.
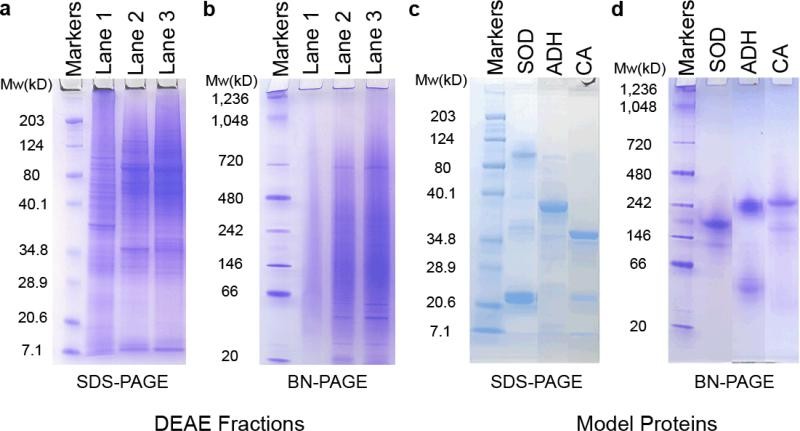
- Electrophoresis: proteins can be separated based on their charge and size by running them through an electric field in a gel matrix. This includes techniques such as polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and SDS-PAGE.
Throughout the purification process, it is important to monitor the protein's purity and concentration using techniques such as SDS-PAGE, Western blotting, or mass spectrometry.
Once a highly pure protein sample has been obtained, it is important to store it properly to preserve its activity and stability. This typically involves freezing the protein sample in a buffer containing a stabilizer, such as glycerol, and storing it at -80°C.
In summary, protein purification is a multi-step process that involves breaking cells open to release proteins, removing cellular debris and non-specific proteins, and using specific techniques to selectively separate the target protein from other proteins in the mixture. The final purified protein sample should be of high purity, high concentration, and stored properly to preserve its activity and stability.
Image from: Metallomics. 2014 May; 6(5): 1068–1078. doi: 10.1039/c4mt00033a
Whether you're looking to create a new purification method or looking for cost-effective purification resins. Contact me today or visit Agarose Bead Technologies (ABT) (www.abtbeads.com) to learn more!
#protein #biotech #research #biology #pharma #abttechnologies
Sales Manager Pharma & Biotech (fine chemicals, intermediates, APIs, excipients, custom projects)
11moDear Miguel Interesting initiative, I'm willing to read next steps, Franco Franco