Seven years ago, an NGO, a team of craniofacial surgeons and a community of host families in Shreveport, Louisiana, moved mountains to bring Farid and Qoosay Salout from Gaza to the US for medical treatment.
The surgeries were a resounding success.
But on 8 November 2023, 12-year-old Farid and Qoosay, 14, were killed in an Israeli airstrike.
The trajectory of the Salout boys’ fight to save themselves from the ravages of a rare medical condition only to die a violent death is a portrait of the profound limitations of life in Gaza long before the war began and of the disproportionate toll the war has had on children.

Nearly 15,000 people have been killed by Israeli strikes in Gaza; the UN estimates two-thirds of them are women and children.
It was in 2016 that five-year-old Farid Salout and his brother Qoosay, then seven, received their version of a golden ticket: an all-expenses paid trip to the US for medical treatment.
Both boys were born with severe craniofacial issues and a disorder that left their eyes abnormally far apart. For babies born with their condition, surgical intervention would ideally start in the first year of life. But there wasn’t a single surgeon in Gaza who could perform the risky and highly specialized procedures the boys needed.
As small children, Farid and Qoosay were happy and well-adjusted kids who liked race cars and wrestling. But without surgery, the boys’ brains would grow without the room needed in their skulls, potentially killing them or leaving them brain damaged.
The Gaza Strip is largely cut off from the world. After Hamas’s electoral victory in 2006, Israel imposed a strict land, sea and air blockade that has been going on for 17 years now, contributing to a series of wars between the two, of which this one is the fifth and most devastating.
The conditions of life in Gaza since Hamas took over and the blockade was imposed are staggering: over half the population lives in poverty and 46% are unemployed. Before the current war, 80% of people in Gaza relied on international humanitarian aid for food.
Primary care is almost non-existent in Gaza – by extension the same is true of preventive care and early intervention when someone does have a medical issue.
Drugs are also hard to come by as a result of the blockade. From 2019 to 2021, only 55% of essential medicines were available in the Central Drugs Store of Gaza’s ministry of health. In 2021, 69% of requests for the entry of X-ray and CT equipment and parts were denied.
It was into this reality that the Salout boys were born. Without outside intervention, they didn’t stand a chance.
That’s where an organization called The Palestine Children’s Relief Fund stepped in. Founded by an American man named Steve Sosebee in 1992, PCRF sends Palestinian children abroad for medical care. They have arranged for more than 2,000 children to travel for treatment for procedures ranging from reconstructive surgery due to war injuries, to conditions that need specialized surgery like the Salout boys’ craniosynostosis.
The hurdles to getting the necessary immigration approvals for someone in Gaza to leave the territory are expensive, cumbersome and not always successful. From 2018 to 2021, 43% of permit applications for a parent or companion of a sick child to go abroad were either explicitly denied or not approved, resulting in a child traveling with a different relative or not at all.
After receiving a special permit to enter Israel for a visa interview at the US embassy, the Salout brothers and their adult companion – their grandmother – were approved to travel. Then there was the issue of getting them ready for the journey.
The boys’ grandmother had never been on a plane. She had to go through what a PCRF patient advocate described as an “extensive, extensive” orientation to explain the concept of baggage claim, the fact that she can’t unilaterally change her seat in a plane, turbulence and other quirks of air travel. For their first flight to the US, Farid and Qoosay’s grandmother dressed them up in three-piece suits.

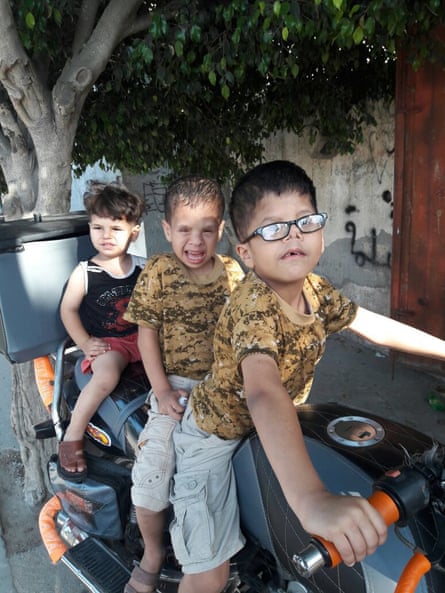
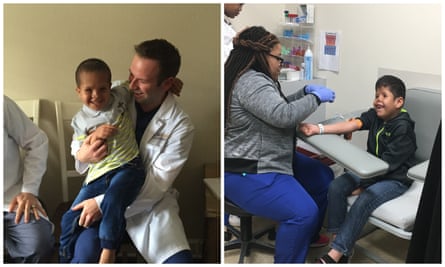
PCRF had enlisted a team of craniofacial specialists at Willis-Knighton Health System in Shreveport, Louisiana, who performed two 16-hour surgeries on the boys at no cost. Dr Ghali Ghali, a renowned oral and maxillofacial surgeon, and a team of specialists removed the front part of Qoosay’s skull to relieve the pressure on his brain. They brought Farid’s eye sockets together and reconstructed his nose.
During their long recovery at the hospital, Farid in particular became a favorite of Ghali’s nursing staff. “Farid, he was a goofball. He liked to joke around a lot. He liked to be tickled,” said Ghali.
Sara Rammouni, a resident of Shreveport and part of the Muslim community there, was tapped by PCRF to make Farid, Qoosay and their grandmother feel at home during their time there and shuttle them to their doctor appointments. They became regulars at the Rammouni home.
Rammouni’s memories are now tinged with guilt for not knowing more about where the family had come from. She recalled an interaction with Farid’s grandmother while they were doing dishes in the kitchen that first week. “She was so surprised by how strong the water flow was. Then she turns around and asks: ‘So when do they cut off the water? And I was like, they don’t. And she was like, ‘Well, what about your electricity?’”
Belal Abujami, a distant cousin of Farid and Qoosay’s father who lived in San Diego at the time, visited the boys in Shreveport after their operation. “The family was crazy happy. They both looked much better and I’d been told by their dad when they went back to Gaza that their personalities had changed. They were more themselves around other kids. They were able to live their lives without medical suffering.”
On 8 November, Farid, Qoosay, their little brother, their father and six other relatives were killed when an airstrike hit their four-story building in the city of Khan Younis in southern Gaza. Relatives say the three had only been at the house for 10 minutes to retrieve items to take back to the school where they were sheltering when the bomb hit.
In photos of the home after it was hit, all that remains is a pancaked slab of concrete.

It took three days to recover the bodies of Qoosay, his brother Qasim and their father. But Farid was never found. His body remains under the rubble.
After the strike, Abujami, their US-based relative, would call his mother in Gaza every day to check in and ask if they’d found Farid’s body yet. The idea of the boy being unclaimed like that, without a proper burial, disturbed him.
But the construction equipment that this effort would require is in rare supply and reserved not for the dead, but for those who can be rescued. “We have to worry about the people who are alive,” Abujami’s mother texted him. Abujami stopped asking after that.
Ghali, who operated on the boys, learned that Farid and Qoosay were killed from my email to his secretary asking for an interview. When Ghali got to the practice that day, he found his entire staff in tears. “There is a lot of effort that is put in to make someone better, more comfortable, happier. Regardless of who they are and where they are from,” he said. “It’s just so sad.”
Rammouni found out about Farid and Qoosay’s deaths from a WhatApp message from their grandmother: “Farid, Qoosay, his brother and father are dead,” it read. “I sat for seven hours straight in the same spot that day,” she told me. “How do I tell my kids that these kids didn’t get to live, they didn’t get to survive? They got the surgery that they needed, but they didn’t get to survive. They didn’t get to grow up.”

She recalled a moment in her living room with the boys’ grandmother, who was on FaceTime making fun of her daughter – Farid’s mom – for having eight kids. Rammouni joined in.
“Stop having babies!” the two told Farid’s mom playfully.
“You know half our children don’t survive,” Farid’s mom kicked back, using a word in Arabic that also means “to live a life”.
Sara is haunted by what then seemed like a dark joke. “Those words from the mom – half our kids don’t survive, they don’t get to live. That kept playing in my head.” she says.
“And she ended up being right. Half her kids, they didn’t survive.”
